[Wiki] OpenZFS cheatsheet
ZFS infos
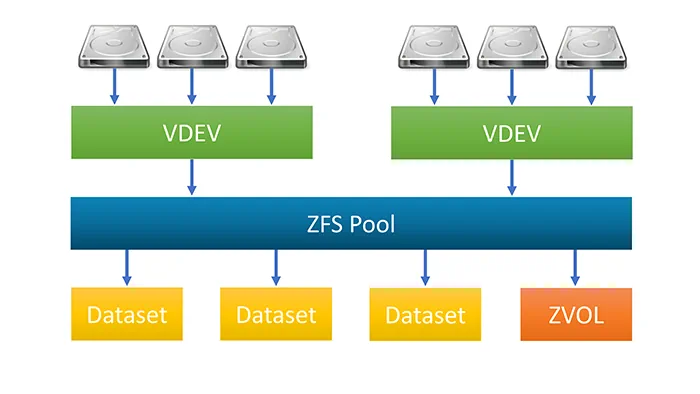
ZFS (Zettabyte File System)
Advanced file system that combines both file system and volume manager functionalities
It offers features like data integrity checks, efficient storage, snapshots, compression, and more
I use it on proxmox & pfsense, more or less on a default configuration
ZIL (ZFS Intent Log)
The ZIL records synchronous write operations in a small, fast log before they are committed to the main ZFS array.
Ensures that these synchronous writes are logged safely to disk
Provide crash recovery in the event of a failure
When a failure happens, ZIL can replay the lost transactions
ZIL SLOG (Separate Log Device)
The SLOG is a dedicated device (typically a fast SSD or NVMe) that can be added to offload the ZIL from the slower main pool disks
Only holds the ZIL for synchronous writes, not all writes
Flushed frequently, and only used during the write confirmation period, does not function like a traditional cache
Beneficial in environments where many synchronous writes happen (e.g., databases, virtual machines)
If you mostly do asynchronous writes, a SLOG may not provide much benefit
It is highly recommended to mirror your SLOG in RAID1 to prevent data loss. If the SLOG device fails without mirroring, you may lose uncommitted write transactions
ARC (Adaptive Replacement Cache)
ARC is ZFS’s in-memory cache that stores recently read data to improve performance.
Resides in system’s DRAM , low-latency access to frequently accessed data.
Highly efficient and uses algorithms to store the most relevant data for fast access.
L2ARC (Level 2 ARC)
L2ARC is an extension of the ARC, residing on fast storage like SSDs or NVMe devices, providing a larger but slightly slower cache compared to ARC.
Used to cache less frequently accessed data than what is in the ARC, reducing the need to fetch data from the primary pool storage.
Consumes some RAM from ARC to manage it. Generally, 1-2% of the L2ARC size is needed in DRAM (ARC) for metadata management
for a 100 GB L2ARC, you might need 1-2 GB of RAM
May not be needed for all ZFS configurations.
Special Device (Special Allocation Class)
The Special Allocation Class is a ZFS feature that allows you to dedicate a fast device (usually an SSD) for metadata and small files, improving performance.
Benefit: It helps speed up access to metadata (file structure information) and small files (typically less than 128 KB)
Removing it without proper migration can lead to data loss
Won’t necessarily speed up the entire pool, but will make operations involving metadata or small files faster
Commands & Infos
Proxmox
With the disk cache set to “writeback,” L2ARC is bypassed, causing I/O spikes and poor VM performance. Setting it to “none” allows L2ARC use, improving boot speed and VM operations.
Commands
Pools
- Create a RAID0 pool
1
zpool create yourpoolname /dev/sdX /dev/sdY
- Create a RAIDZ1 pool
1
zpool create yourpoolname raidz1 /dev/sdX /dev/sdY /dev/sdK
- Create a RAIDZ2 pool
1
zpool create yourpoolname raidz2 /dev/sdX /dev/sdY /dev/sdK
- Create a mirror pool with /dev/sdX /dev/sdY in mirror and /dev/sdK /dev/sdZ in mirror
1
zpool create yourpoolname mirror /dev/sdX /dev/sdY mirror /dev/sdK /dev/sdZ
- Add disk to a pool
1
zpool add yourpoolname /dev/sdX
- Expand a pool
1
zpool online -e yourpoolname /dev/sdX - Destroy a Pool
1
zpool destroy yourpoolname
- Export/Import a pool
1 2
zpool export yourpoolname zpool export yourpoolname
Datasets
- Create a dataset
1
zfs create yourpoolname/datasetname
- Set Dataset Properties (e.g., compression)
1 2
zfs set compression=on yourpoolname/datasetname zfs set compression=lz4 yourpoolname/datasetname
- Create a snapshot named 12jan2014 of the datasetname filesystem
1
zfs snapshot yourpoolname/datasetname@12jan2014
- List Snapshots, then rolleback
1 2
zfs list -t snapshot zfs rollback poolname/datasetname@snapshotname
Informations Gathering
- ZFS pool infos
1 2 3
zpool status zfs get all yourpoolname zpool history - ZFS list dataset
1
zfs list
Performances
- Display detailed ZFS I/O statistics every 2 seconds
1 2
zpool iostat 2 zpool iostat -v 2
1
2
arc_summary
arcstat
- Scrub a Pool (data integrity check)
1
zpool scrub yourpoolname
L2ARC & ZIL(SLOG)
- Add a ZIL (SLOG) Device
1
zpool add yourpoolname log /dev/sdX
- Add an L2ARC Cache Device
1
zpool add yourpoolname cache /dev/sdX
- Remove Cache Device (L2ARC)
1
zpool remove yourpoolname cache /dev/sdX
- ARC configuration in /etc/modprobe.d/zfs.conf
1 2 3 4
# 2 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 = 2147483648 = 2GB options zfs zfs_arc_min=2147483648 # 4 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024 = 4294967296 = 4GB options zfs zfs_arc_max=4294967296
after modification -> update-initramfs -u -k all a reboot is required
- L2ARC configuration in /etc/modprobe.d/zfs.conf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
# Maximum amount of data written to L2ARC per second # 64 MB/s * 1024 * 1024 options zfs l2arc_write_max=67108864 # Extra data written to L2ARC during the initial warmup period options zfs l2arc_write_boost=134217728 # Ratio of metadata in L2ARC, placed in RAM options zfs l2arc_headroom=4
after modification -> update-initramfs -u -k all a reboot is required
To continue
- Add link to a “Lab or practice”