[Project] Coraza-SPOA and Owasp Coreruleset on HAproxy
Installing Coraza and use case with OWASP CRS + haproxy
I had to choose a frontend for my website, sometimes not using services, and I selected HAProxy for various reasons that I won’t elaborate on here. Additionally, I wanted it to provide broad WAF filtering. So, here’s a blog post about HAProxy and the implementation of Coraza with OWASP rules.
1. Installing HAproxy
You can use : https://haproxy.debian.net/
In my case I wanted the last version of haproxy in LTS release so the 3.0.0 at this time.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
sudo apt update
sudo apt install curl gpg
sudo su
curl https://haproxy.debian.net/bernat.debian.org.gpg | gpg --dearmor > /usr/share/keyrings/haproxy.debian.net.gpg && echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/haproxy.debian.net.gpg] http://haproxy.debian.net bookworm-backports-3.0 main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/haproxy.list
exit
sudo apt update
sudo apt install haproxy=3.0.\*
2. Installation of Coraza-SPOA
GO installation, check lastest stable here : wget https://go.dev/dl/
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
wget https://go.dev/dl/go1.23.5.linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.23.5.linux-amd64.tar.gz
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
echo 'export GOPATH=$HOME/go' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
#This command should return the version if everything is good
go version
Here we start the installation of Coraza SPOA :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
sudo apt install git make gcc pkg-config wget unzip
git clone https://github.com/corazawaf/coraza-spoa.git
cd ./coraza-spoa
#compilation
go run mage.go build
# create user and group
addgroup --quiet --system coraza-spoa
adduser --quiet --system --ingroup coraza-spoa --no-create-home --home /nonexistent --disabled-password coraza-spoa
We are not over yet, even if we have compiled coraza spoa, we still need to create te directory and copy configuration files and even activate the service, let’s go :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
mkdir -p /etc/coraza-spoa
cd /etc/coraza-spoa
#Check latest version : https://github.com/coreruleset/coreruleset/releases
sudo wget https://github.com/coreruleset/coreruleset/archive/refs/tags/v4.10.0.zip
mkdir -p /var/log/coraza-spoa /var/log/coraza-spoa/audit
touch /var/log/coraza-spoa/server.log /var/log/coraza-spoa/error.log /var/log/coraza-spoa/audit.log /var/log/coraza-spoa/debug.log
cp -a ./build/coraza-spoa /usr/bin/coraza-spoa
chmod 750 /usr/bin/coraza-spoa
cp -a ./example/coraza-spoa.yaml /etc/coraza-spoa/config.yaml
sed -i 's/bind: 0.0.0.0:9000/bind: 127.0.0.1:9000/' /etc/coraza-spoa/config.yaml
sed -i 's|log_file:.*|log_file: /var/log/coraza-spoa/coraza-agent.log|' /etc/coraza-spoa/config.yaml
Good, now we have a default installation
3. Coraza integration with HAproxy
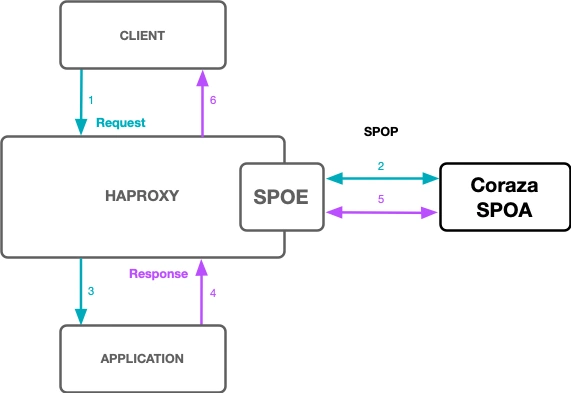
SPOE: Stream Processing Offload Engine.
SPOA: Stream Processing Offload Agent.
SPOP: Stream Processing Offload Protocol.
WAF: Web Application Firewall.
HAproxy integrate the SPOE to send requests and receive reponse to/from the SPOA, used for processing.
Communication between SPOE and the SPOA happens via the SPOP (2 & 5). The result of the scan is sent back to HAProxy to authorize or block the traffic.
Configuration files
- /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg - HAProxy Main Configuration
- /etc/haproxy/coraza.cfg - HAProxy SPOE Configuration
- /etc/coraza-spoa/config.yml - Coraza SPOA Main Configuration
- /etc/coraza-spoa/coraza.conf - Coraza Engine Configuration
CRS Rules syntax
TO simplify or schematise :
SecRule is a directive like any other understood by ModSecurity and Coraza integrates theses.
A SecRule is made up of 4 parts :
- Variables - Instructs ModSecurity where to look (sometimes called Targets)
- Operators - Instructs ModSecurity when to trigger a match
- Transformations - Instructs ModSecurity how it should normalize variable data
- Actions - Instructs ModSecurity what to do if a rule matches
The structure of the rule is as follows:
SecRule VARIABLES “OPERATOR” “TRANSFORMATIONS,ACTIONS” A very basic rule looks as follows:
1
SecRule REQUEST_URI "@streq /index.php" "id:1,phase:1,t:lowercase,deny"
Phases
ModSecurity processes security rules in 5 main phases during the Apache request cycle.
These phases allow different types of checks to be made at specific points, and secure the web application by detecting and blocking malicious requests or responses.
Let’s break it down:
Request Headers: First stage where the server reads the incoming request headers from the client.
Request Body: Once the headers are read, ModSecurity then processes the body of the request. This is where most application-specific security rules are applied.
Response Headers: In this phase, ModSecurity checks the headers before sending the response back to the client.
Response Body: After headers are set, ModSecurity checks the body of the response, looking for sensitive information or errors before it reaches the client.
Logging: Finally, after all other checks, ModSecurity logs the transaction and can modify how the logging is handled.
To continue
- ansible playbook
- Logs handling
- Disable Rules, make exception for an IP address
- IP reputation, blocklist
- Exclusion for nextcloud or others services
- Phase 1 and Phase 2 to explain
- more details on conf files